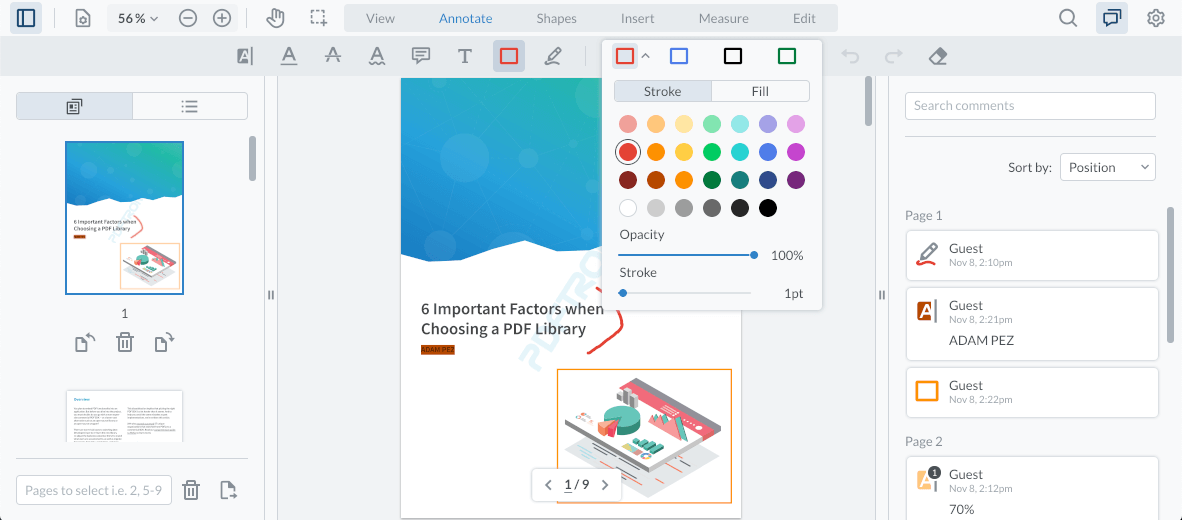
A complete and responsive user interface is provided out of the box in the WebViewer download package, allowing you to quickly get started integrating a document viewer into your web app. Zooming, thumbnails, searching, annotation tools and comments are just a few of the features provided by the UI.
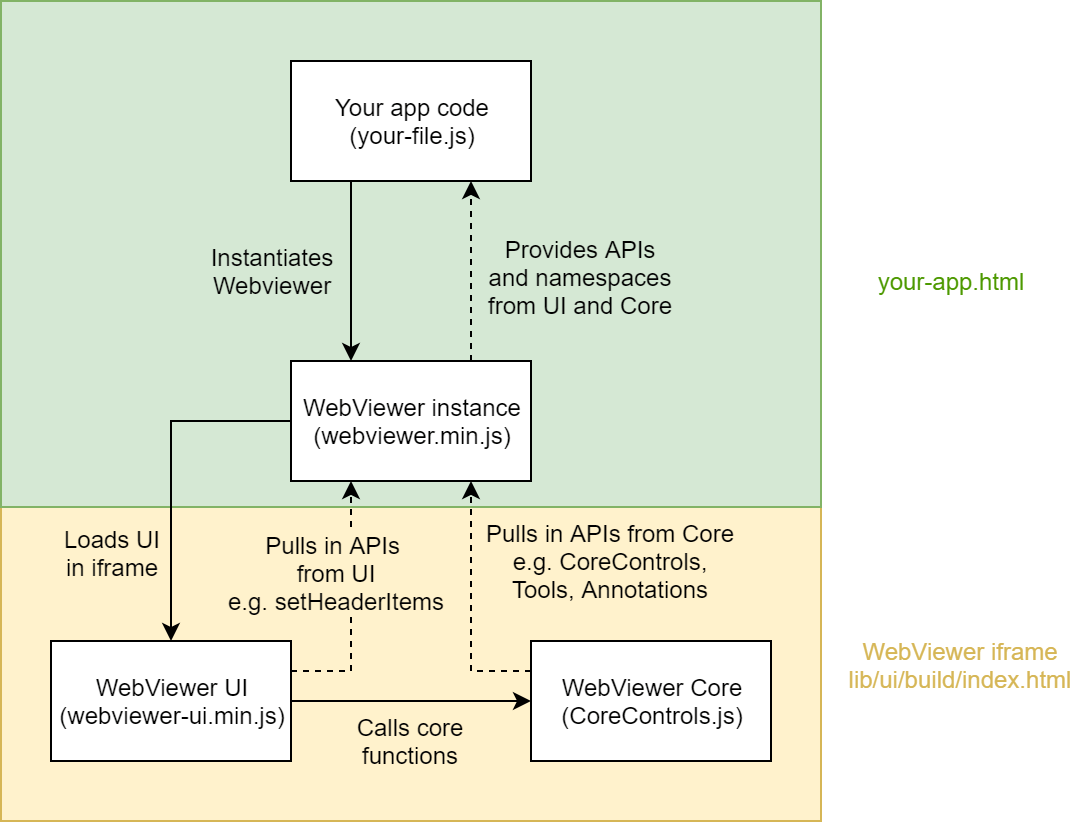
APIs are provided to allow you to customize the look and feel of the UI and the code is open source for more advanced customizations. The UI uses WebViewer's core document APIs to handle rendering and document manipulation.
How it works behind the scenes
When using the UI your web app HTML page might look something like this:
<!-- Your app's HTML page -->
<html>
<head>
<script src="my-app-code.js"></script>
<script src="webviewer/lib/webviewer.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- viewerElement passed to WebViewer -->
<div id="viewer">
</div>
</body>
</html>
When the page loads, webviewer.min.js will create an iframe inside the specified viewer element with the src set to the WebViewer UI's index.html:
<div id="viewer">
<iframe src="webviewer/lib/ui/build/index.html#d=...">
<html>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- The WebViewer UI and document scrollview elements -->
</div>
<!-- The WebViewer core JS library -->
<script src="../../core/CoreControls.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
</iframe>
</div>
The UI's HTML file loads CoreControls.js and uses those APIs to render the document.
<div id="viewer">
<iframe src="webviewer/lib/ui/build/index.html#d=...">
<html>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- The WebViewer UI and document scrollview elements -->
</div>
<!-- The WebViewer core JS library -->
<script src="../../core/webviewer-core.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
</iframe>
</div>
The UI's HTML file loads webviewer-core.min.js and uses those APIs to render the document.