PDF.js Express Web Viewer has three measurement tools, with each of them having a scale ratio and precision. These properties can be changed using the UI or programmatically.
Set scale and precision with the UI
To set measurement properties for a tool, click on the measurement tool icon and select the tool. A style menu will pop up in which you can find and change the properties.
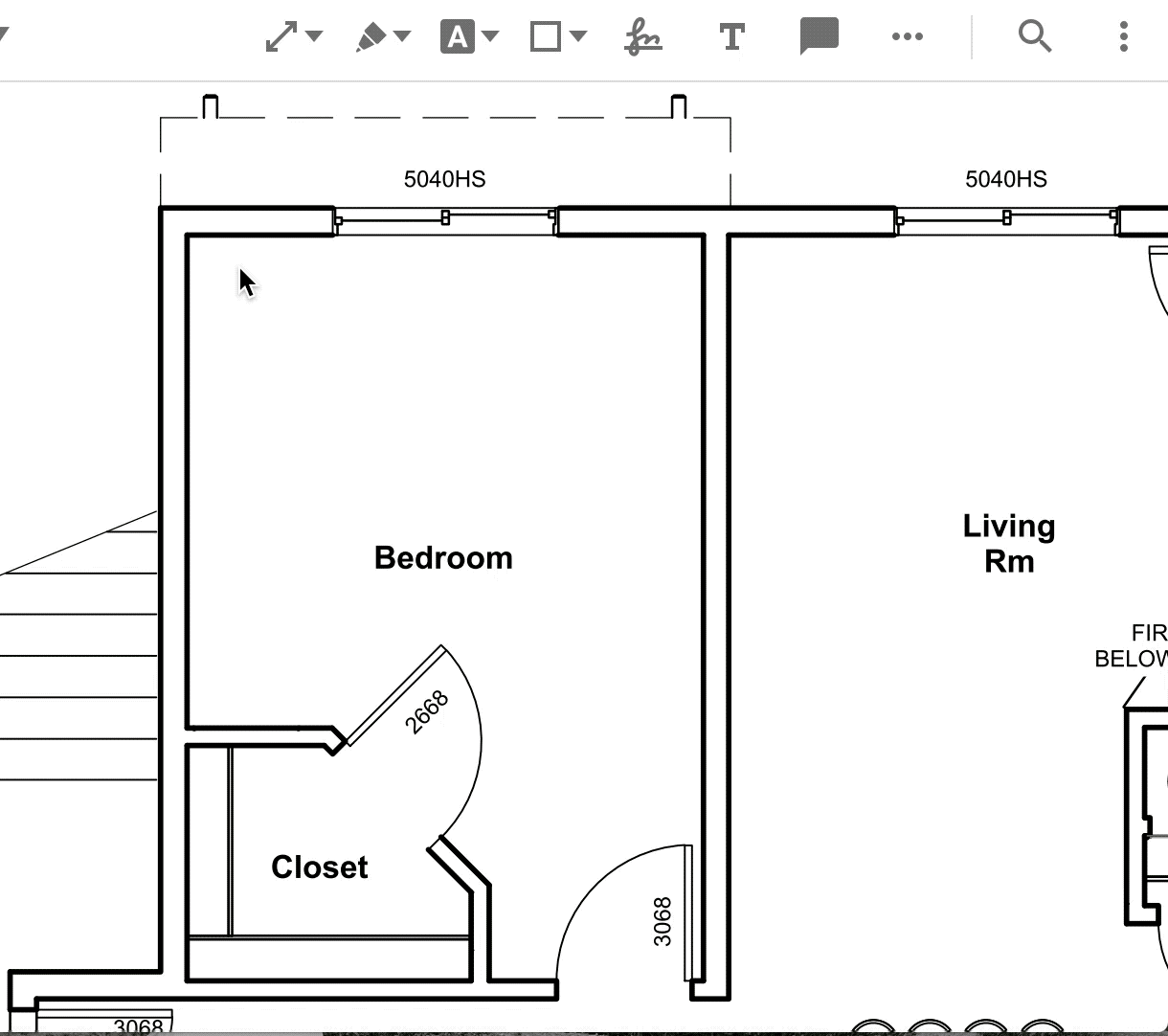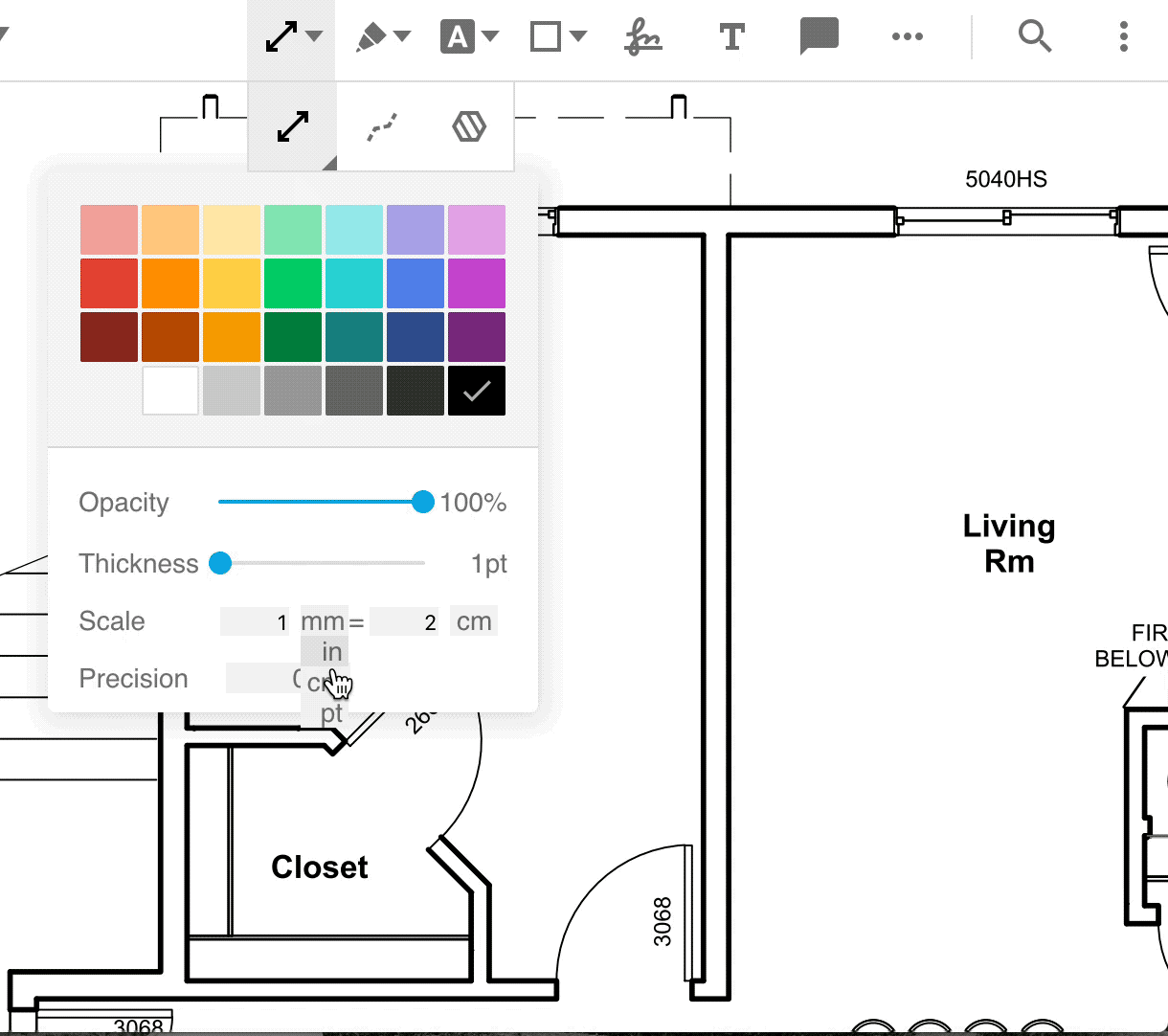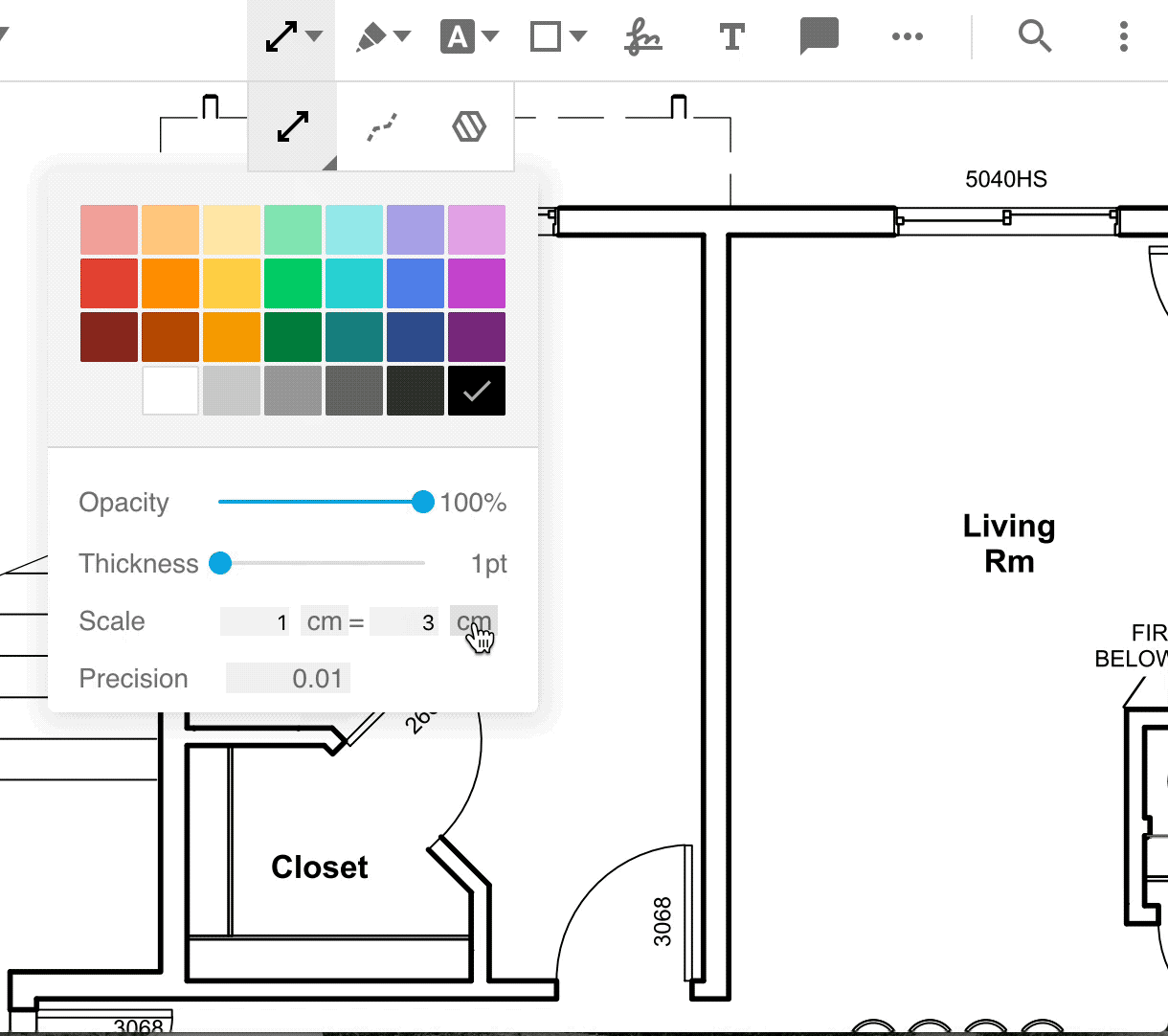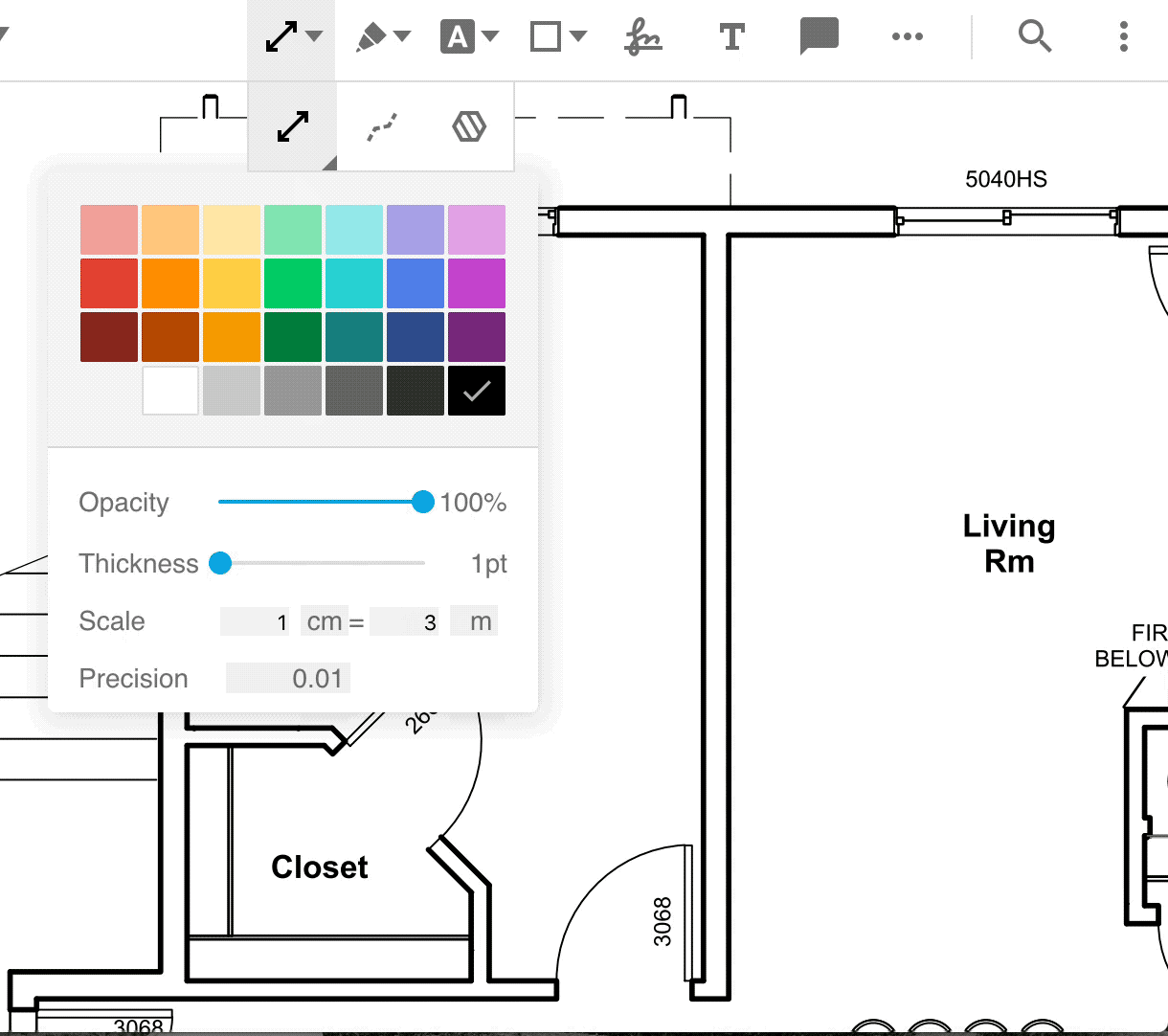
Set scale and precision programmatically
You can take the same approach as shown in the Customizing tools guide to set measurement properties. Measurement related tool names are: AnnotationCreateDistanceMeasurement, AnnotationCreatePerimeterMeasurement and AnnotationCreateAreaMeasurement. You can view the list of valid tool names here. The following example sets the scale and precision of the distance measurement tool:
WebViewer(...)
.then(instance => {
const { docViewer } = instance;
const distanceMeasurementTool = docViewer.getTool('AnnotationCreateDistanceMeasurement');
distanceMeasurementTool.setStyles(() => ({
// value of Scale is an array that is consisted of two arrays
// the first element in each array is the scale ratio and the second element is the unit.
// valid units are: mm, cm, m, km, mi, yd, ft, in and pt
// the following array means that for the annotations created by the distance measurement tool, 0.25 inches on the document is equal to 1 inch in the real world
Scale: [[0.25, 'in'], [1, 'in']],
// value of Precision is a number that means how many decimal places the calculated value should have
Precision: 0.001
});
);
});
WebViewer(...)
.then(instance => {
const { documentViewer } = instance.Core;
const distanceMeasurementTool = documentViewer.getTool('AnnotationCreateDistanceMeasurement');
distanceMeasurementTool.setStyles(() => ({
// value of Scale is an array that is consisted of two arrays
// the first element in each array is the scale ratio and the second element is the unit.
// valid units are: mm, cm, m, km, mi, yd, ft, in and pt
// the following array means that for the annotations created by the distance measurement tool, 0.25 inches on the document is equal to 1 inch in the real world
Scale: [[0.25, 'in'], [1, 'in']],
// value of Precision is a number that means how many decimal places the calculated value should have
Precision: 0.001
});
);
});
Get scale and precision programmatically
The following example logs the precision and scale of the distance measurement tool:
WebViewer(...)
.then(instance => {
const { docViewer } = instance;
const distanceMeasurementTool = docViewer.getTool('AnnotationCreateDistanceMeasurement');
console.log(distanceMeasurementTool.defaults.Scale);
console.log(distanceMeasurementTool.defaults.Precision);
});
WebViewer(...)
.then(instance => {
const { documentViewer } = instance.Core;
const distanceMeasurementTool = documentViewer.getTool('AnnotationCreateDistanceMeasurement');
console.log(distanceMeasurementTool.defaults.Scale);
console.log(distanceMeasurementTool.defaults.Precision);
});

